With the rise of the internet, new technologies, and social media, the global numerical data (also known as quantitative data) and categorical data production volume continues to skyrocket. This is known as the Big Data. Nowadays, organisations are constantly generating and collecting data, with one goal: to transform this "black gold" into actionable insights for better decision-making. This is how data analysis has developed within organisations. This science, which involves examining raw data to draw conclusions, has become popularised across all business functions, procurement departments in particular.
What is data interpretation?
Data interpretation, also known as data analysis, involves analysing raw data through various techniques to extract relevant new information. It is a process that covers the collection, organisation, and interpretation of large data volumes. This concept relies on a range of analysis tools, technologies, and processes.
Upstream, data modelling is used to prepare the data for analysis. This approach involves creating a visual representation (such as pie charts or bar charts, for example) to define the data collection and management systems within an organisation.
Through the analysis of a data set, organisations can better understand past events, but also prepare for, or even shape, the future. More specifically, they will be able to draw conclusions, solve problems, or identify trends. Ultimately, this is how they can make better decisions to ensure the longevity of their activities.
Interpreting data has an extremely broad scope of application. Every business's field is concerned: marketing, customer experience, finance, production, human resources... Procurement is no exception, with a key objective: contributing to the company's competitiveness.
Various types of data interpretation
Organisations can interpret data through several types of analytics. These complementary analyses reflect various levels of complexity and added value and provide clear data-driven answers to fundamental questions raised.
Descriptive analysis
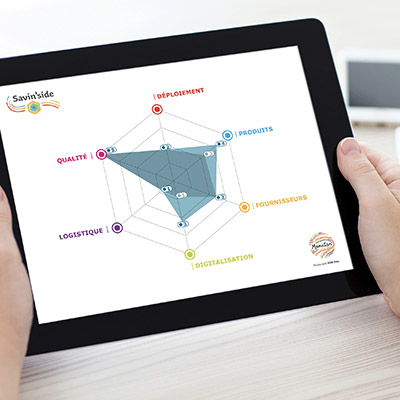
Descriptive analysis features a data overview to provide information on what happened. With this data analysis process, we answer a key question: what happened? These are basic methods (average numbers, percentages, standard deviation...) that deliver factual results, useful for evaluating a company's performance. Descriptive analysis is at the heart of reporting, business intelligence solutions, dashboards with graphs and diagrams... In procurement, this may include reports on monthly expenditure, for example.
Diagnostic analysis
Diagnostic analysis seeks to understand the reasons why something happened, particularly those that have the most impact. Here, we answer another key question: why did it happen? This mostly focuses on exploring the data and correlations between various data points. In the context of procurement, it can help identify the underlying causes of cost variations or delays in the supply chain.
Predictive analysis
As its name suggests, predictive analysis allows for the prediction of future outcomes, as well as the assessment of the probability that they will occur, based on historical data associated with other information. The idea is to answer the question, "What is likely to happen?"
By using data mining, we can predict future trends. This allows us to anticipate potential risks and identify opportunities within the company, and thus prepare accordingly. In procurement, it can help predict price variations, changes in demand, and market developments. Decision-makers can then adjust their strategy accordingly.
Prescriptive analysis
Prescriptive analysis aims to identify actions to be implemented based on the predictions made. This answers the more complex question: what should be done? This type of analysis relies on both advanced statistical methods and new technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence or Machine Learning.
Prescriptive analysis goes further than predictive analytics because it allows for testing multiple hypotheses. In the context of procurement, it can suggest adjustments in the supply chain, alternative suppliers, or cost-saving opportunities.
Data interpretation in service of procurement
Being at the heart of the company's ecosystem, the procurement function has access to a multitude of data. When properly exploited, the collected data holds tremendous opportunities for optimising its strategy.
Optimise expenditure
Expenditure analysis is a strategic mission for procurement departments. This involves tracking and classifying expenditure by suppliers as well as by product and service categories to identify areas for optimisation and cost reduction. This data can also be cross-referenced with market trends (market studies, price indices...) to seize new opportunities. It is an essential lever for improving the company's competitiveness.
Boost processes
Through data analytics, procurement departments can also optimise and rationalise their processes. By examining the resources used, the procurement journey, or internal customers behavioural patterns, they can review their operations to streamline tasks, gain efficiency, and shorten lead times.
Manage supplier performance
This analysis process also allows for an in-depth evaluation of supplier performance. Based on key criteria such as quality, reliability, and compliance, buyers can adjust their supplier selection, renegotiate contracts, and improve their relationships with their partners.
Evaluate procurement performance
It is imperative to measure procurement performance via key performance indicators (KPIs). Data analysis then focuses on cost reduction, adherence to allocated budgets, or internal demand satisfaction. This is how procurement departments can objectively evaluate their contribution to the company's overall strategy.
Data interpretation is now essential in business. Within procurement departments, this data science is particularly exploited to make more informed and proactive procurement decisions, reduce unnecessary expenditure, improve risk management, and identify new cost-saving opportunities. In this sense, it is a powerful tool for strengthening companies' competitiveness and differentiation, and thus contributing to their long-term success and development.