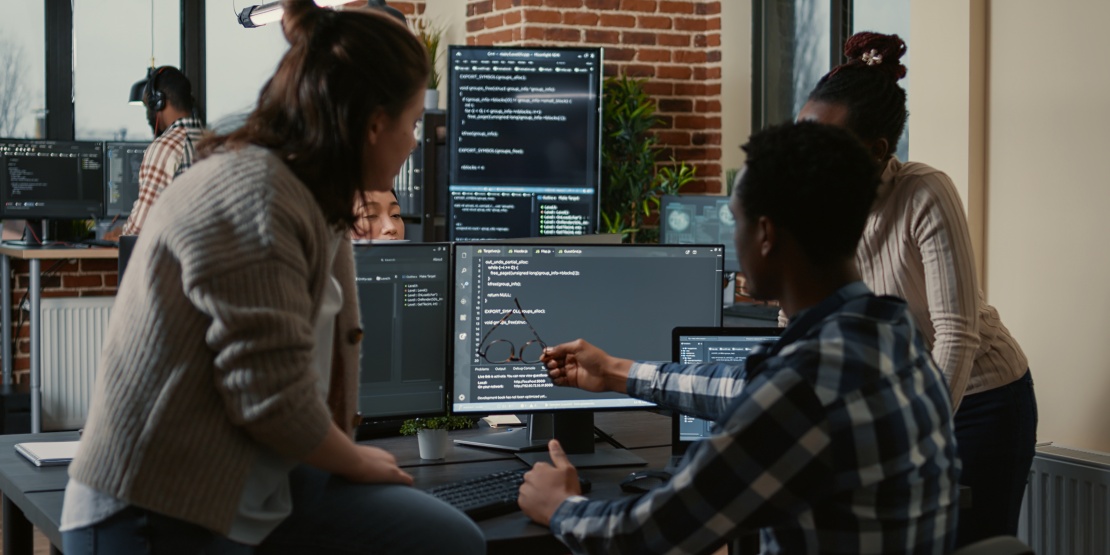
Companies are increasingly turning to new computing devices to speed up performance and tackle complex market challenges. This is particularly true for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and one of its subfields: Machine Learning (ML). This digital tool can interpret large volumes of data using advanced algorithms to make predictions, improve existing processes, and solve problems. Machine learning enables businesses to optimise supply chain management and all its component activities, opening up tremendous opportunities for growth and efficiency.
Machine learning: Definition
Also known as 'automated learning', machine learning (ML) aims to give machines the ability to learn from data using artificial neural networks. This data can be words, numbers, statistics, images, or any other form of information that can be digitally processed. It's a field of study within Artificial Intelligence (AI) as this software system simulates learning, which is a form of human intelligence.
When faced with a variety of situations, the machine learning technology extracts valuable information from a set of training data. Machine learning requires an exposition to evermore data to gradually learn which decision is correct and create a model that achieves the best quality performance over time for accomplishing the assigned task. Once the learning phase is complete, the model can then be put into production.
As a subfield of AI, machine learning is particularly effective at finding trends or correlations, making decisions or making predictions from vast amounts of diverse and changing data. As you've understood, machine learning applications improve with experience. And the larger the volume of accessible data, the more precise these applications become. It's especially useful in fields like data science, where the goal is to extract insights from big data and perform predictive analytics.
How does machine learning work?
Developing machine learning models involves four main steps, from selecting the training data set to using and improving the model.
Selecting training data
The first step involves selecting and preparing a set of training data. This input data is fed to the machine learning system and allows it to automatically learn about the problem for which it was created. At a minimum, the data must be cleaned and organised. These data points can also be labelled to indicate to the model which characteristics it should consider. It can just as well be unlabelled, in which case the model must identify and extract these features on its own.
Selecting the algorithm
The second step involves selecting the algorithm that will be run on the training data. The choice of algorithm depends on several factors such as the type and volume of data to identify, as well as the nature of the problem to be solved. Common machine learning algorithms include support vector machines, decision trees, and linear regression.
Training the algorithm
The third step involves training the algorithm. Variables are run through the algorithm, the results are compared with what should have been obtained, and then adjustments are made to acquire accurate results. This process continues until the algorithm is capable of producing an output that meets the teams' requirements. This is how the machines learn without being explicitly programmed.
Using and improving the model
The fourth step paves the way for using and improving the model. The idea is to train the model on a new dataset associated with the problem to be solved. Over time, efficiency and accuracy can improve as the machine learning model is exposed to more real-world data.
Different types of machine learning
Algorithms power automated machine learning systems. Today, several types of algorithms are used to train machine learning in business: Supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. These different machine learning models are distinguished by the nature of the data used and the desired result.
Supervised machine learning
Supervised learning algorithms are the most common model. In this case, the model is guided by data scientists in the conclusions it should draw. The algorithms learn through a labelled dataset with a previously defined result.
Unsupervised machine learning
Through unsupervised learning algorithms, the computer learns to identify complex patterns and processes without constant and rigorous control and guidance from the data scientist. This therefore involves basic training with unlabelled data and no associated result. Clustering algorithms is a common example of unsupervised learning.
Semi-supervised machine learning
Unsurprisingly, semi-supervised learning is a clever mix of the two previous models. During training, a small set of labelled data is used to guide classification algorithms, as well as a larger set of unlabelled data to extract features.
Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning is similar to supervised learning. However, the machine learning algorithms are trained by proceeding through trials, errors, and rewards rather than using a dataset. In this approach, the reward is programmed into the algorithms as an element to be collected.
Machine learning: What applications in the warehouse?
Fabrice Bonneau, partner-founder of the Argon & Co consultancy, explains: "AI today encompasses very different subjects and domains. Machine learning, for example, has long been exploiting internal and external data, pattern recognition, to make sales and workload forecasts, etc. What's new is that AI is now beginning to permeate industry, maintenance, etc. The core use cases of the supply chain."
Better forecasting demand
First, machine learning can accurately predict demand by analysing consumption data (order contents, consumer preferences, sales trends, etc.). This allows the company to adapt its procurement and stock management processes accordingly.
Improving risk management
Using machine learning also allows for the detection of situations that involve potential risks. This takes several forms: Delivery delays, supply chain disruptions, demand fluctuations, etc. The company can then implement preventive strategies.
Boosting predictive maintenance
Experts use machine learning tools to monitor the condition of connected products, self-driving cars, and machines. By conducting a comprehensive data analysis, this technology can evaluate their durability and proper functioning. Once again, the company is able to act proactively to avoid a potential stoppage of the supply chain. This is an example of how machine learning can be used to make decisions and predict future outcomes.
Machine learning thus offers tremendous opportunities to transform the management of your company and, in particular, your warehouse by automating and optimising its processes. From improving customer experience to enhancing operational efficiency, the applications of machine learning are vast and continually expanding.