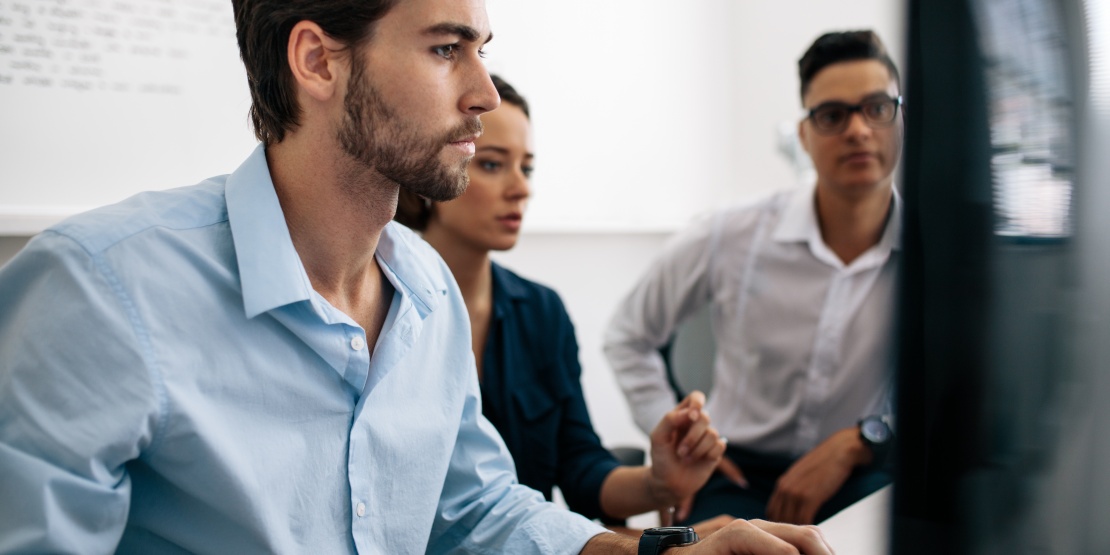
In today’s digital age, companies are accelerating the digitisation of their procurement processes. This now concerns the entire Source-to-Pay (S2P) process, which covers all activities between a company and its suppliers, ranging from the strategic sourcing of partners to the payment of invoices. The aim is to adopt a strategic approach to optimise the procurement life cycle as much as possible through technological solutions. This is how procurement departments intend to generate value for their company.
Definition of Source-to-Pay (S2P)
Also known as "S2P", Source-to-Pay refers to the sourcing and procurement process within organisations. It involves selecting suppliers, committing to a commercial relationship with them, and buying goods and services that meet the organisation’s needs. It encompasses the entire procurement life cycle, from sourcing and selecting suppliers (Source) to paying invoices (Pay).
This process thus involves multiple stakeholders in the value chain: The procurement function, of course, but also finance, accounting, legal, suppliers, and requisitioners from various departments within the organisation. For companies, the objective is to optimise each stage to improve efficiency and maximise profits.
The key stages of the Source-to-Pay (S2P) process
For any organisation, the S2P process starts with the need to choose, renew, or deepen a relationship with a supplier. It can be broken down into two main parts: Source-to-Contract and Procure-to-Pay. Each comprises essential steps to ensure the effective management of procurement processes.
Source-to-Contract (S2C)
Firstly, the Source-to-Pay process focuses on the upstream activities before the act of buying. This covers the entire Source-to-Contract (S2C) part.
(Insert a diagram using the graphics below, which evokes a process, and add the words in yellow + associate an icon with each stage)

The Source-to-Pay process
------------------Source-to-Contract------------------------- / -----------Procure-to-Pay--------------------
1. Sourcing > 2. Contractualisation > 3. Supplier management > 4. Procurement request > 5. Purchase order > 6. Invoice
Sourcing
This first stage involves researching, assessing, and identifying potential suppliers as part of a data analysis or a specific request. Buyers issue a request for proposal and assess the bids based on predefined criteria (price, quality, lead times, sustainability, etc.). They then negotiate the terms and select the supplier best suited to meet their requirements.
Contract conclusion
Once the supplier is selected, buyers formalise the commercial relationship through a contract. This document governs the collaboration and defines the rights and obligations of each party, ensuring mutual commitment. In the case of indirect procurement, framework agreements are often preferred as they offer flexibility.
Supplier management
Buyers can then integrate the supplier into their database, with all associated information (contact details, products and services, negotiated prices, performance evaluations, etc.). This stage also involves monitoring the supplier’s performance as well as the relationship and contract management on an ongoing basis.
Procure-to-Pay (P2P)
Secondly, the Source-to-Pay process focuses on formalising the company’s needs and the transaction with the supplier. This is commonly known as the Procure-to-Pay (P2P) process, which is often associated with e-procurement solutions to digitise the transactional part.
Procurement request
A procurement request represents the expression of a need by an internal customer. They search an approved catalogue (typically a Punch-Out) to identify the goods or services required for their activities. Once the products are selected, they fill a cart, which is then transformed into a procurement request. The procurement department reviews and approves the request if it complies with company policies.
Purchase order
When the procurement request is approved, it generates a purchase order that is sent to the supplier. Upon receiving the order, the company ensures the conformity of the delivered products and/or services compared to the initial specifications. The company must notify the supplier of any discrepancies or disputes, if applicable.
Invoice processing
Finally, the last stage concerns the management of invoices and payments. When the company receives the invoice, it matches it against the purchase order and/or delivery note, validates it, and proceeds with payment to the supplier. It then archives the document and updates the supplier’s account.
The essential digitisation of the S2P process
Nowadays, many solutions exist in the market to digitise the entire the Source-to-Pay process or parts of it. Whether distinct modules or an integrated suite, these tools are now necessary in any corporate procurement strategy and synonymous with undeniable advantages.
Process optimisation
The digitisation of the S2P process allows for optimisation of the entire procurement cycle, or even automation of certain steps such as issuing requests for proposals, creating contracts, matching invoices, etc. This contributes to reducing lead times, increasing team productivity, and minimising human errors. Overall, it promotes operational efficiency.
Cost reduction
S2P solutions also assist the procurement function in reducing administrative costs, negotiating better contractual terms with suppliers, and identifying new opportunities for expenditure management. These are effective levers for achieving direct and indirect cost savings within companies, thus boosting their competitiveness.
Improved overall visibility
Such solutions also provide better visibility across all procurement processes. Data consolidation allows for better expenditure management, but also better supplier performance control and risk management by procurement teams. This promotes transparency and informed decision-making.
Solid collaboration with suppliers
Lastly, S2P solutions foster fluid and effective communication between procurement teams and suppliers. This enables improved collaboration, building strong relationships, or even strategic long-term partnerships. It is important to remember that maintaining good business relationships is a source of innovation, efficiency, and mutual added value for each party.
As you can see, procurement departments have every interest in relying on a digital solution to boost their Source-to-Pay (S2P) processes. This is how they can improve their operational efficiency, but also strengthen their competitiveness in the market. As every supply chain becomes increasingly complex, S2P solutions are emerging as a formidable lever for performance.