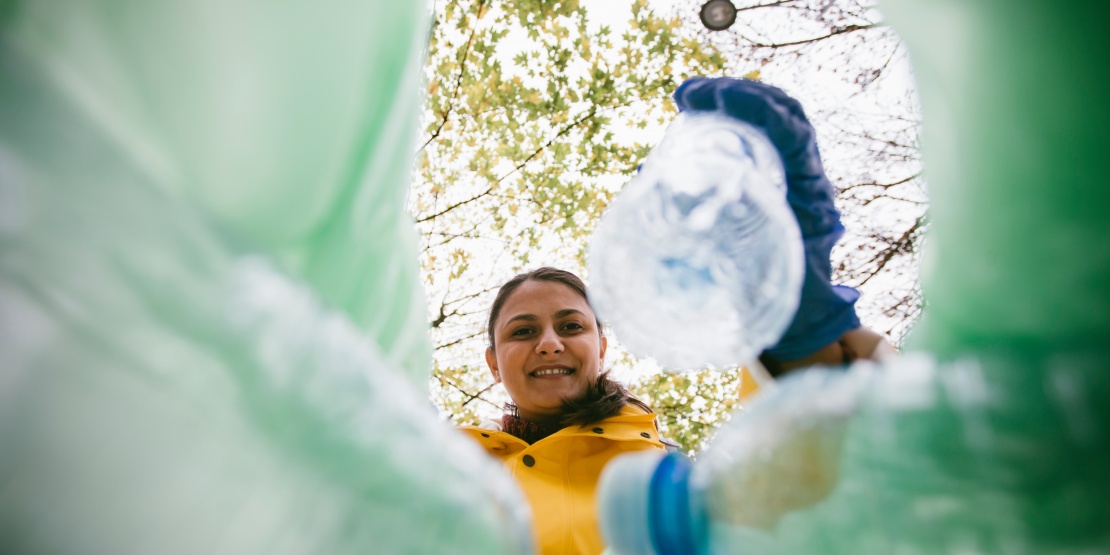
Today, waste management represents a major environmental and societal challenge. In business as elsewhere, it becomes imperative to limit the quantity of waste generated, but also to recover it within a circular economy logic. Beyond complying with regulatory requirements, it's about reducing the impact on the environment and natural resources to contribute to a sustainable future.
Waste recovery: the key to waste management
For a business, good waste management consists of identifying, sorting and recovering materials from its activities. All whilst respecting regulatory obligations and optimising resource utilisation.
Whether dealing with household waste or industrial waste, waste management is based on a clear hierarchy of treatment methods. This begins with prevention, as the best waste is that which doesn't exist! This is followed by preparation for reuse, then recycling and other types of recovery, such as energy recovery and finally, disposal. The idea is to maximise environmental, social and economic benefits, whilst minimising negative impacts and costs.
Today, waste recovery is an essential component of waste management. According to the waste framework directive 2008/98/EC, this designates "any operation whose main result is that waste serves useful purposes by replacing other materials that would have been used for a particular purpose, or that waste is prepared to be used for that purpose, in the plant or in the economy as a whole." In other words, this involves removing waste from its traditional sorting and treatment circuit to substitute other substances, raw materials or products.[1]
The different types of waste in business
Businesses produce different types of waste:
- Household waste: paper, cardboard, packaging, food remains...
- Economic activity waste: manufacturing debris, used materials...
- Hazardous waste: chemicals, batteries, waste oils...
- Inert waste: concrete, bricks, tiles...
- Other waste: non-hazardous electronic waste, plant waste...
What are the various types of waste recovery?
We distinguish four main types of waste recovery.
Recovery through reuse
The first type of recovery is reuse and reutilisation. When goods are in a satisfactory condition, they can be repaired, cleaned, refurbished... to be put back on the market. When we speak of reuse, goods haven't gone through the "waste" stage and are used again for a similar purpose. When it comes to "reutilisation", products become waste and are reused, sometimes for a different purpose. This takes the form of second-hand office furniture, refurbished phones, etc.
Material recovery
Material recovery is waste recycling in its most concrete form. It involves treating waste in order to reintroduce some of their materials into a production cycle. We can recycle a wide variety of materials: metals, plastics, glass, cardboard, paper, wood, textiles, etc. Each stream requires specific treatment, often carried out in specialised recovery units.
Energy recovery
When waste cannot be recycled, it can then be used for energy production. This is what we call energy recovery of waste. Several techniques exist: incineration, pyrolysis, methanisation... Energy recovery can then produce energy in the form of heat, electricity, or even fuel, thus substituting fossil fuels. Stéphane Leterrier, Managing Director of Paprec Énergies, comments: "Generating energy from waste is essential to meet the environmental and geopolitical challenges of this century".
Organic recovery
Lastly, organic recovery concerns all biodegradable waste: food waste, green waste, agricultural waste, etc. The principle: naturally transforming organic matter, through composting or methanisation, into natural fertiliser. The idea is that this waste can be returned to the earth to nourish new crops.
Best practices for recovering waste in business
To successfully conduct your waste recovery approach, there are essentials. This involves employee engagement, formalisation by procurement teams and partner selection.
Training and raising awareness amongst employees
First of all, it's essential to involve all teams within your business. This involves training them in best practices for waste management and sorting, but also raising awareness of the issues this raises. Businesses can implement information campaigns, clear signage or collaborative workshops like the Waste Fresco. Inspired by the Climate Fresco, this fun tool helps participants better understand the waste management system as well as impacts on the environment.
Integrating recovery into your sustainable procurement policy
Procurement also has a key role to play in waste reduction and recovery. This involves formalising expectations and requirements of the business at the heart of the sustainable procurement policy. We can, for example, integrate specific environmental criteria, such as repairability, provision of spare parts... in order to favour more responsible products, and, above all, better recoverable ones. We can also require collection of old equipment in our tender, or favour equipment rental.
This was the case for the Olympic and Paralympic Games Organising Committee (COJOP) which rented a large part of its technological equipment (computers, printers, televisions...) and which had also planned a second life solution for most of the purchased equipment.
Collaborating with the right partners
Lastly, waste recovery requires identifying and partnering with the right stakeholders. Depending on the sector's maturity, these players can intervene at different levels: flow auditing, sorting implementation, selective collection, waste treatment and recovery... All whilst respecting regulations and with a view to cost optimisation. It's important to favour a service provider who guarantees responsible practices, ensures end-to-end traceability and measures achieved performance.
Recover your equipment with Manutan
The Manutan Group supports you in collecting and recovering your furniture and electronic equipment. This turnkey service guarantees offering the best possible second life to your equipment. Depending on their condition, we can buy them back from you, donate them to an association or recycle them whilst respecting the environment. As a result, we provide you with a CSR report that quantifies carbon emission savings and professional integration hours funded through the operation.
Today, it's imperative to produce better, consume better, and of course better manage our waste. This requires collective mobilisation: employees, buyers, suppliers, service providers... This is how businesses can strengthen their resilience, but also position themselves as committed players in favour of sustainable development.
[1] Stéphane LETERRIER, (Managing Director, Paprec Energies), Energy recovery of waste: A solution for the future, PAPREC, https://www.paprec.com/fr/solutions/les-solutions-de-valorisation/la-valorisation-energetique/