Through digital tools, e-procurement leverages technology to digitise business transactions between companies and suppliers to better manage and improve the efficiency of the procurement process. In this article, find out everything you need to know about e-procurement in order to have all the tools that you need to implement it effectively within your company.
How is e-procurement defined?
E-procurement is “the centralised management of a company's procurement and supply chain using an electronic platform”. The “e” stands for “electronic”. It is also sometimes known as supplier exchange.
It is important to keep in mind that e-procurement is only suitable for business purchases, meaning the Business to Business (B2B) sector. It is not used in the Business to Customer (B2C) sector, which concerns only personal purchases.
The software and information systems that e-procurement uses enable the purchases to become paperless for all or part of the Procure-to-Pay process (P2P), which has three main phases:
- Selection of goods;
- Sending the order;
- Invoicing and payment.
What is e-sourcing?
It is important to note that e-procurement is considered separately from e-sourcing, which focuses on the Source to Contract (S2C) process. E-sourcing uses digital tools to digitise the Source to Contract process, which involves the identification and selection of suppliers.
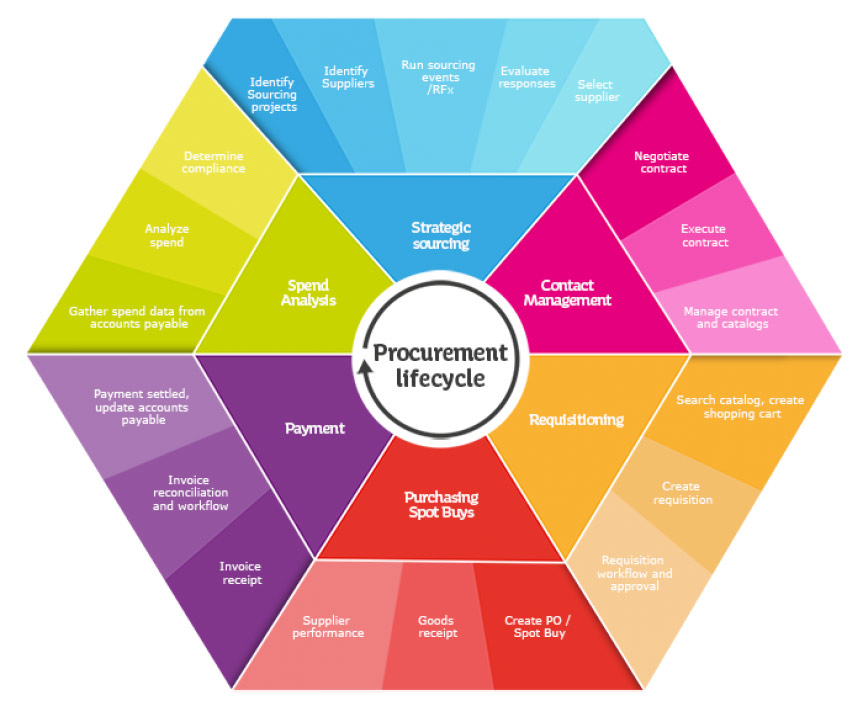
The procurement life cycle
Who is e-procurement for?
E-procurement is mainly the domain of four different groups within companies:
- The procurement department which defines and optimises the procurement strategy;
- The end users who are the source of the need, those who place the order;
- The person who approves orders;
- The financial and accounting departments, which reconcile orders and invoices and make payments.
How does e-procurement work?
E-procurement can be broken down into three main steps that are specific to the Procure-to-Pay process.
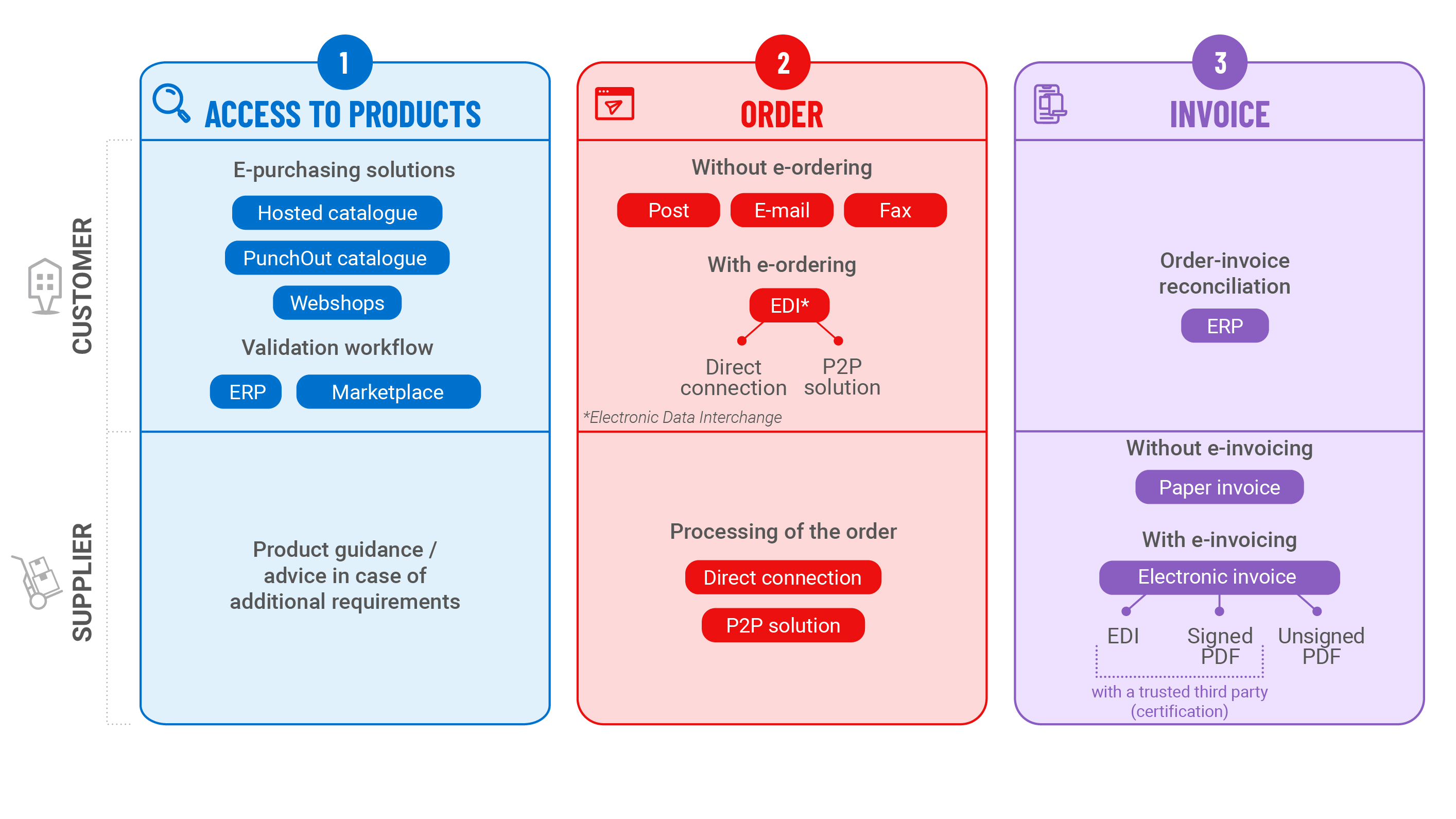
1. Selection of goods
Companies visit a specific platform, which may be an online catalogue, a Punch-Out[1] or a B2B vendor website. This gives them access to the supplier's entire offer, including data about the contractual conditions (products selected, cost, savings, etc.).
They select their products and send their purchase request with just a click. This request then enters their procurement system and follows the predetermined approval process.
2. Sending the order
Once it has been approved, the purchase request becomes an order. It is automatically sent to the supplier in the form of an electronic document or through a marketplace. The supplier then instantly begins to prepare the products for delivery.
3. Receipt of the invoice
Invoicing can also be paperless: companies receive the invoice that has been certified by a trusted third party in the form of a PDF file or an electronic document, which is automatically reconciled with the order and triggers the payment.
What are the objectives of e-procurement?
E-procurement centralises and automates interactions between stakeholders (end users, procurement department, suppliers, etc.) in order to improve the performance of the procurement process, management and strategy. There are four major benefits.
1. Savings
The cost of a standard transaction is estimated at an average of £80 and that of a 100% digital transaction (from product selection to payment) at less than £16[2]. One reason for this is the reduction in the cost of labour resources, since the process is fully automated. Relative to the number of orders, especially for indirect purchases, the savings are considerable.
2. Eliminate low value-added processes
Getting rid of administrative and manual tasks is a strategic way to increase teams’ speed and efficiency, while reducing the rate of error by an average of 30-50%[3]. With e-procurement, sending the purchase order, requesting approval, reconciling the order and the invoice... They’re all automated. This allows teams to focus their energy on tasks with higher added value.
3. Shortening the overall timeframe
Whether placing orders or approving them, the process is streamlined and gives companies more transparency: there is no more down time, reminders, or handling and filing of administrative documents. This saves considerable time in the procurement process.
Furthermore, since the order is converted directly into a preparation slip for the supplier, companies ultimately receive their goods more quickly.
4. Controlled spending
E-procurement provides better visibility, with a clear, real-time view of spending (principals, procurement process, etc.) through reporting features. This means they can:
- Better manage their spending;
- Manage costs and budgets more accurately;
- Adjust their strategy by identifying areas for improvement.
What are the advantages and constraints of a digital procurement process?
Of the many benefits that e-procurement offers, savings on invoicing are at the top of the list. Costs are reduced through the digitisation of procurement procedures, which optimises business transactions between companies and suppliers.
It is also a real management tool since it allows buyers to stop wasting their energy on time-consuming and low-value-added tasks and enables them to focus on their core business. The quality of the services provided by the procurement department is thus improved and the employees’ productivity enriches.
However, e-procurement requires a detailed study of procurement software and service procurement systems that are available before it can be implemented. The objective for an e-procurement tool is to have every actor in the procurement chain be involved.
Another constraint of this business solution is the e-procurement software itself. These workflow management systems can be cumbersome for users.
Suppliers, for their part, must adapt to the order placement tools that their customers require of them, and are forced to provide an electronic catalogue.
- Download our white paper "Purchasing policy and CSR"