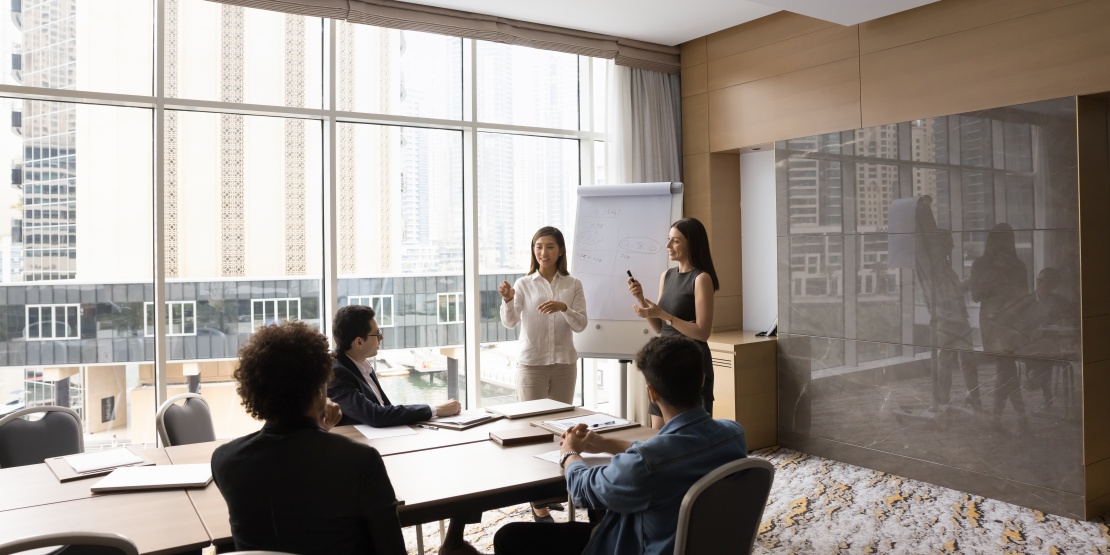
In an ever-changing economic environment, information management has become strategic. Organisations must understand market dynamics, anticipate changes, and make informed decisions based on available information. This is where competitive intelligence (CI) comes into play. This strategic approach allows organisations to collect, analyse and exploit useful information to enhance their competitiveness.
Competitive intelligence: Definition and pillars
Competitive intelligence (CI) refers to the organised process of collecting, analysing and disseminating all useful information to economic actors. For companies, this approach aims to anticipate market developments, detect opportunities and threats, with the goal of strengthening their competitiveness. Knowing and forecasting are thus the two watchwords of competitive intelligence. Competitive intelligence relies on three fundamental pillars: strategic monitoring, economic security, and influence.
Strategic monitoring
Strategic monitoring involves researching, collecting and analysing relevant information about a company's environment.
This may include:
- Competitor intelligence to adjust strategy;
- Technological monitoring to stay ahead of innovations that could impact the business;
- Commercial monitoring to follow consumption trends.
Economic security
Ensuring company security and protecting strategic information are also at the heart of this approach. This requires building a comprehensive security policy that takes into account the different stages of the information lifecycle. The idea is to prevent any threat to the company's security, development and reputation.
Influence
Influence involves using information to shape the market and strengthen the company's visibility. This can take the form of marketing campaigns, strategic partnerships or engagement in the political process. It helps reinforce the company's market position and create an environment favourable to its interests.
The issues of competitive intelligence
Through this tactical and strategic approach, companies gain a significant competitive advantage and are better prepared to meet the challenges they face. This plays a role in their ability to remain competitive, innovative and compliant.
Competitiveness
In a globalised economy with a competitive landscape, competitive intelligence can help companies anticipate market developments by capturing even weak signals. They can identify opportunities and react to threats with full knowledge of the facts, thus strengthening their competitiveness.
Innovation
This approach also promotes innovation by providing strategic information on technological trends and consumer needs, as well as developing networks. It can contribute to the development of new products and/or services or to the improvement of internal processes.
Risk management
Lastly, companies need to use competitive intelligence to be proactive within the regulatory framework. This allows them to:
- Analyse potential risk factors;
- Detect warning signals;
- Evaluate their stakeholders;
- Communicate with authorities;
- React to incidents.
How to initiate a competitive intelligence approach?
Implementing a competitive intelligence approach is organised in six main stages. For it to pay off, it must be driven by management, based on a solid ethical framework and supported by all employees.
1. Setting a framework
The first step is to define a clear competitive intelligence strategy, diagnose information needs and draft specifications. It is also important to raise awareness among all employees and designate a responsible person as a reference.
2. Monitoring your environment
Next, it is necessary to build an action plan that organises the collection of information. This involves defining information sources, learning to master them, and then automating your monitoring system. This necessarily involves implementing dedicated competitive intelligence tools and training the relevant employees on the importance of competitive intelligence.
3. Analysing information
Among the data collected, strategic information must be identified. This is then subjected to selective processing, within a short timeframe, while taking into account potential cognitive biases. During this competitive intelligence analysis, analysts, potentially supported by a community of experts, interpret the results to draw valuable insights.
4. Managing information
The challenge is to transform this information into actionable knowledge. To do this, it must be communicated, disseminated, shared, enriched... Knowledge only has value when it circulates within the company. Everyone must be able to make sense of it in their business context.
5. Protecting yourself
Throughout this process, it is crucial to ensure the protection of intangible assets, namely strategic information, as well as the company's know-how and image. This involves self-diagnosing vulnerabilities and developing a solid cybersecurity culture. Remember: company employees are the first line of defence.
6. Influencing your environment
At this point, the company is able to use this knowledge as a lever for action to promote its interests, while respecting the legal framework.
This may involve:
- Internal communication to mobilise employees;
- Activating press relations to establish its image;
- Preparing crisis communication to strengthen risk management;
- Influencing public decisions (commonly known as lobbying).
As you can see, a new economic revolution is underway, based on strategic information and knowledge. In this context, competitive intelligence is emerging as a powerful lever for companies wishing to enhance their competitiveness and resilience. It is even essential for navigating a volatile, uncertain, complex and ambiguous (VUCA) world like ours. By adopting a proactive approach, decision-makers can transform information into a major strategic asset, paving the way for sustainable growth and a leading market position.