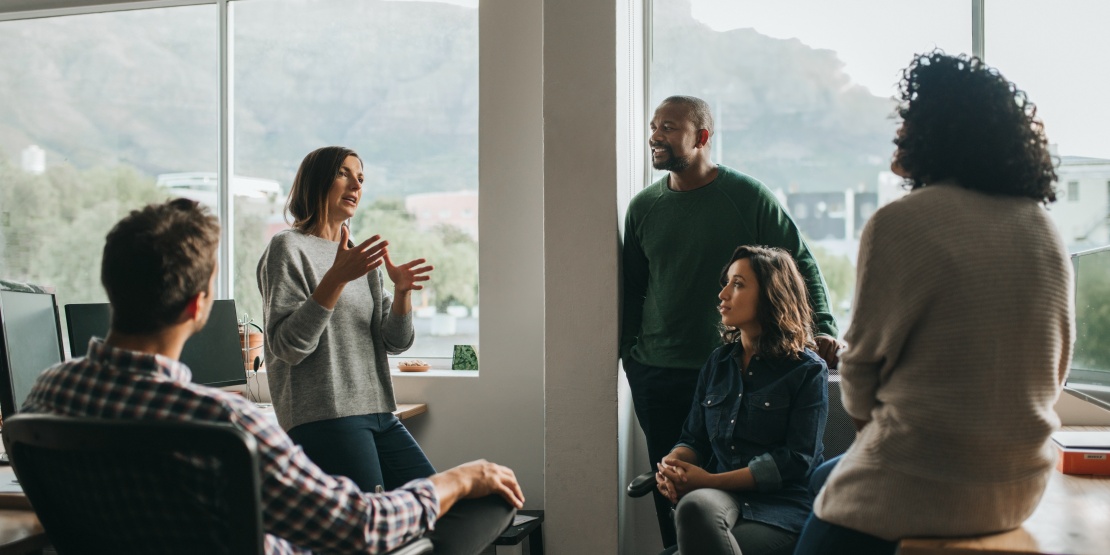
In today's competitive environment, process optimisation has become a top priority for companies. To remain competitive, they strive to reduce costs, improve quality and increase operational efficiency. It is in this context that Lean Six Sigma proves to be a particularly powerful approach. By combining Lean and Six Sigma principles, this methodology eliminates waste, reduces variations and defects, thereby improving overall performance.
Lean Six Sigma: definition, origins and foundations
The term "Lean Six Sigma" refers to the convergence of two well-known process improvement methods in the business world: Lean and Six Sigma. While Lean aims to eliminate waste, Six Sigma focuses on reducing variability and defects. Together, these two methodologies improve business process quality and efficiency, serving customer satisfaction.
Lean Management, against tasks without added value
Lean Management is a management methodology that originated in Toyota's production system. Its main objective is to improve company performance, particularly the quality and profitability of production. This method focuses on eliminating waste to increase added value for the customer.
In Lean Management, there are three main types of waste.
Muda
These are activities that consume resources but provide no added value for the customer (overproduction, waiting times, unnecessary movements, non-quality...).
Muri
This refers to an overload or overexploitation of resources, which can lead to malfunctions, accidents or slowdowns, for example.
Mura
This waste is characterised by irregularity, which can hinder production fluidity.
Six Sigma, for process reliability
Six Sigma, on the other hand, is a quality management methodology developed by Motorola. The idea is to improve the process of a repetitive task through data measurement. Its goal is to reduce process variability and eliminate defects through a systematic approach.
Very concretely, combining the Lean method and the Six Sigma method consists of "getting it right the first time" without unnecessary expenses and delays, to obtain the greatest customer satisfaction.
The advantages of Lean Six Sigma
When these two process-oriented approaches, Lean and Six Sigma, are jointly implemented, their benefits complement each other. The Lean Six Sigma methodology thus becomes a formidable lever for improving customer service and overall profitability.
Reduce costs
One of the major advantages of Lean Six Sigma is significant cost reduction. By eliminating defects and steps that add no value, companies can reduce their operating costs.
Improve quality
Through this method, companies strive to rationalise and standardise their processes to reduce waste and defects. This inevitably translates into a greater number of products and/or services of better quality. At the end of this process, it improves customer satisfaction and thus provides a competitive advantage.
Boost performance
Implementing Lean Six Sigma also improves the companies' overall performance. They perfect their processes and maximise their efforts to deliver a highly performing product and/or service, accelerating production and delivery cycles. This is how they gain in efficiency, but also in productivity.
Involve teams
This method leads companies to develop a true continuous improvement culture. In this dynamic, teams are particularly engaged in the approach. Such a mindset strengthens the sense of belonging, as well as collective motivation and performance.
Lean Six Sigma: how to implement it?
Deployed in project mode, Lean Six Sigma relies on the problem-solving method called "DMAIC". It's a pragmatic approach based on five main steps, namely: Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control.
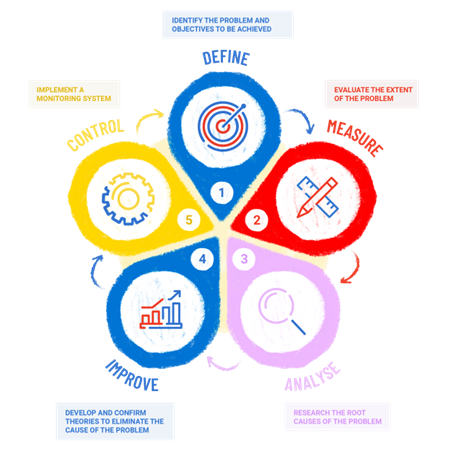
Alt tag: "DMAIC" method diagram
Define
It all starts with identifying the problem and the objectives to be achieved. It's important to understand the pain points and/or expectations of customers. This also involves defining the scope, deadlines and project team.
Measure
Next, the project team evaluates the extent of the problem through an indicator: service rate, off-contract purchase rate... By collecting the necessary information, this allows them to measure its impact.
Analyse
It's then a matter of researching the root causes of the problem using precise techniques such as process analysis and/or data analysis.
Improve
The project team develops and confirms theories to eliminate the cause of the problem. They start by testing solutions before implementing them permanently.
Control
Lastly, it's important to ensure that the solution works in the long term. This involves monitoring the results obtained by implementing a monitoring and control system with a process management dashboard.
Lean Six Sigma is a key methodology for ensuring continuous and systematic improvement of business processes. By combining Six Sigma and Lean principles, it's possible to create more robust, faster and more efficient processes. It's a formidable lever for productivity, customer satisfaction and cost reduction. The future of companies lies in their ability to innovate and continuously optimise their operations, and Lean Six Sigma methodologies are indispensable tools to achieve this.