Today, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a true lever for overall performance. Many studies show that CSR is closely linked to business success. However, it is not always easy to quantify the benefits of programmes and initiatives in this area. To measure the return on investment of their CSR approach, businesses must look well beyond the financial dimension. It involves assessing the overall impact on value creation, both for the company itself and, more broadly, for its ecosystem.
ROI beyond the financial dimension
Today, it has become essential for every company to measure the ROI (return on investment) of its sustainability initiatives in order to guide decision-making, allocate budgets and sustain this approach. It is about justifying investments, strengthening corporate credibility and demonstrating that Corporate Social Responsibility is indeed a source of value, not a burden, for companies.
Expert quote
"In a company, CSR initiatives number in the dozens. Some have a strategic character, others fall under operational management, whilst others still come within the scope of philanthropy. For a company, it is necessary to focus on eight to twelve essential criteria, for which the economic and financial repercussions will be, if not easy, at least possible to determine. Turnover, capital productivity, risk management: we must achieve a positive ROI. Otherwise, we need to question the validity of CSR."
- Philippe Cornet, CSR consultant trainer
But beyond financial performance, returns on investment also touch upon environmental and social aspects. This is what Luc Wise, founder of The Good Company, emphasises: "If success is only financial, then you are not a responsible company. Success is of course the economic aspect, but also the people I work with - internally, service providers, customers - and the environment." All these elements help strengthen intangible capital (brand image, attractiveness...) and corporate resilience (risk reduction, supply chain robustness...).
It is in this dynamic that social return on investment (SROI) came into being. It allows the measurement and valuation of a company's overall positive impact for a given investment amount. It measures costs as well as social, environmental and economic benefits, then translates them into monetary value to calculate a cost/benefit ratio. SROI thus complements purely accounting and financial return on investment.
Which dimensions can be evaluated?
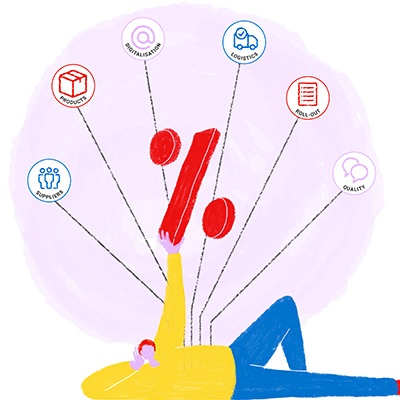
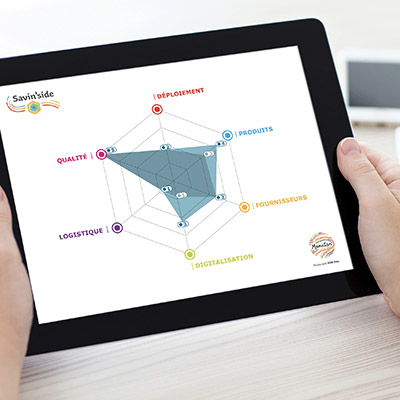
K. Kumar and C. Muthulakshmi, two researchers affiliated with G. Venkataswamy Naidu College, propose a methodological framework to concretely measure the return on investment of CSR initiatives. This covers five key dimensions: revenue, reputation, recruitment, retention and relationships.
Revenue
The main return on investment of CSR is seen in the company's net profit. It involves making savings, acquiring new customers and strengthening their loyalty. This can be achieved through the development of sustainable products or services, the deployment of thematic marketing campaigns, the adoption of green techniques or technologies that contribute to cost savings, optimising energy consumption...
Potential indicators to monitor:
- Number of new customers acquired through the sale of sustainable products or services;
- Savings made thanks to sustainable initiatives;
- Percentage of customers sensitive to CSR issues;
- Revenue generated through the sale of sustainable products or services.
Did you know?
A study conducted by McKinsey & Company and NielsenIQ highlights that products promoting sustainable commitments have recorded stronger growth than others. Over five years, retail sales of these products increased by an average of 6.4% per year, compared with 4.7% for other products.
Reputation
The return on investment of CSR also plays out in the company's image and brand reputation. This naturally involves communicating about CSR initiatives and their concrete impacts, with transparency, accuracy and clarity.
Some typical indicators:
- Number of media mentions regarding CSR initiatives;
- Social media engagement concerning CSR;
- Awards, recognition, certifications received;
- Integration into CSR indices.
Recruitment
One of the key benefits of CSR also relates to attracting the best talent. Nowadays, new generations are increasingly sensitive to their employers' CSR commitments. Human resources must integrate this CSR dimension into recruitment materials, the interview process, etc. To evaluate this type of indicator, surveys must be conducted with new recruits, but also potentially with prospective candidates.
Some examples of indicators:
- Percentage of candidates from CSR-focused recruitment campaigns;
- Percentage of new candidates valuing CSR;
- Percentage of new recruits with CSR-related experience.
Retention
One of the flagship returns on investment of CSR is also found in employee retention. Participating in CSR initiatives gives them a sense of purpose, pride, strengthens collaboration and bonds between them, and leads them to develop new skills. This plays a key role in increasing their long-term loyalty, engagement and overall satisfaction. Again, surveys are the best way to obtain data. This can be done annually or periodically.
Indicators to measure:
- Percentage of employees participating in CSR initiatives;
- Employee satisfaction level regarding CSR initiatives;
- Average length of tenure in the company of employees involved in CSR.
Use case at Manutan
At Manutan, we evaluate the experience and satisfaction of all our employees every year. Through an anonymous questionnaire, we measure the implementation and deployment of our common culture. Among the many questions asked, some relate to CSR. For example, 89% of employees working at headquarters say they are proud of the company's CSR commitment.
Relationships
Lastly, the return on investment of CSR will also focus on building solid partnerships. A company that collaborates with partners on CSR projects will increase its influence on its ecosystem, whilst strengthening ties with them. It is important to share ambitions and commitments regarding CSR to generate support and align practices.
Here is an example of indicators:
- Percentage of suppliers or partners engaged in CSR initiatives;
- Percentage of suppliers who have signed the ethical charter;
- Number of new external relationships created through partnerships with the voluntary sector;
- Value of commercial partnerships arising from CSR initiatives.
In business, measuring and tracking the ROI of CSR is essential to demonstrate that responsibility is inseparable from performance. Far more than a reporting exercise, it enables the adjustment of CSR strategy, sharing of results and engaging the ecosystem. In short, it is the key to a sustainable competitive advantage.