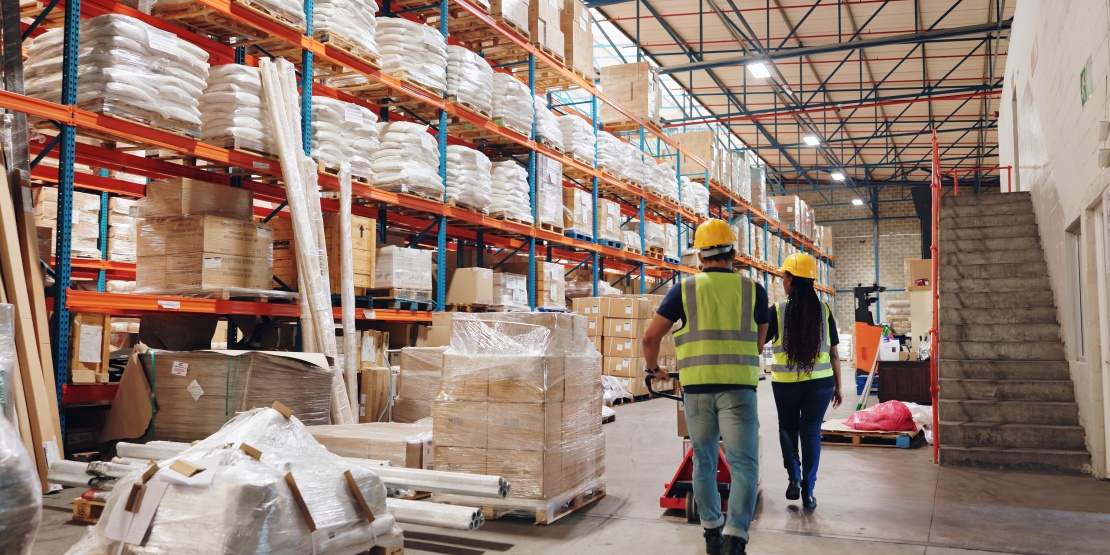
All companies, without exception, follow the procurement cycle to secure the resources needed for operating and developing their activities. This cycle breaks down into five major steps, from identifying your business needs to paying for goods and services. The challenge for organisations is to master each of these phases and leverage the right optimisation strategies to improve productivity, competitiveness, and overall profitability.
What is the procurement cycle?
The procurement cycle refers to the process by which a company orders, obtains and pays for the goods or services it needs, both short and long term. It is also known as the supplier purchase cycle or the Procure-to-Pay (P2P) process. Here we focus on the upstream flow of the supply chain, meaning how the company obtains raw materials, goods and services, from its vendors or suppliers to its own site.
An optimal procurement cycle results in purchasing the right products and/or services in the right place at the right time. The objective is to ensure these processes are standardised and efficient so they can be regularly repeated for purchasing the goods and services necessary for the company.
Lastly, it's important to note that the procurement cycle is an integral part of the broader procurement life cycle, which also includes spend analysis, strategic sourcing, and contract management.
The 5 steps of the procurement process
The procurement cycle follows the same major steps for all types of companies. This spans from reviewing purchasing needs to payment and accounting records.
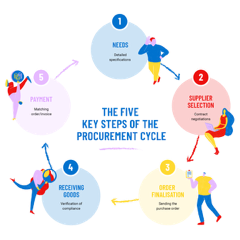
Step 1: Identifying needs
Every procurement cycle begins with identifying a need. This may take the form of procurement requests made by employees and submitted to the procurement department. It involves precisely defining the requirements related to the goods and/or services to be purchased. This includes defining quantities, required standards, and delivery timeframes.
Step 2: Selecting suppliers
The next step of the procurement process is choosing suppliers suited to your needs. You can request offers from potential suppliers through a request for quotation (RFQ). This involves evaluating suppliers according to several criteria: Price, quality, reliability, production capacity... This step also includes negotiating contract terms. For recurring purchases, both parties can establish framework agreements that guarantee purchasing conditions and promote a lasting relationship.
Step 3: Finalising the order
The third step of the procurement cycle consists of placing an order. The procurement request is transformed into a purchase order, which is sent to suppliers. These documents precisely define the products, quantities, and delivery conditions.
Step 4: Receiving goods
The arrival of ordered goods constitutes the fourth step of the procurement cycle. The company must then ensure that the delivery complies with its order, that there was no damage during transport, and that the product quality is correct. The delivery is then recorded and forwarded to the recipient within the company.
Step 5: Proceeding to payment
The last step of the procurement cycle is payment. The payment terms depend on what has been contractually agreed: Advance payment, deposit due before delivery, payment on a certain date, staggered payment... The accounting department records, verifies and posts the invoice before issuing payment authorisation.
How to optimise the procurement cycle?
Procurement departments have several tools at their disposal to optimise all operations related to the procurement of products and services.
Automating as much as possible
One of the most effective levers for optimising your procurement cycle lies in digitalisation, rationalisation and automation of processes. This is possible with the implementation of e-procurement solutions within your company. Such a tool allows for digitalisation of transactions, cost optimisation, and productivity gains. Moreover, it offers complete visibility of the expenses incurred, making them easier to control and helping identify areas for improvement.
Strengthening supplier relationships
The procurement department also benefits from strengthening relationships with key suppliers. This translates into collaboration based on transparency, proximity, and trust. To achieve this, the company must focus on solid communication and regular evaluation of supplier performance and satisfaction, in a continuous improvement approach. This guarantees a long-term relationship where each stakeholder develops.
Focusing on Lean Management
Additionally, it may be wise to rely on the philosophy of Lean Management to optimise processes. Ivalua, an international leader in the spend management solutions market, is convinced of its virtues: "Lean in Procurement and Supply Management can be viewed as a way to improve the procurement process and workflows, reducing time and eliminating waste; reduce costs while improving the quality of products and services; improve the performance and responsiveness of suppliers; increase the focus on those activities that add value to the firm; and enhance procurement’s strategic rather than transactional focus."
Standardising your processes
Lastly, it is important to have standardised processes to optimise your procurement cycle. This involves formalising them as clearly as possible by drafting procedures and documents that will serve as references for the teams concerned. It is important that employees are informed and even trained on these various operations. This is an effective way to make operations more reliable and harmonise practices within the company.
As a result, a well-organised procurement cycle helps reduce risks, control costs, and improve overall procurement performance. The key to success lies in structured management, effective collaboration with suppliers, and the integration of powerful digital tools. This is how the procurement team can create added value, supporting their company.